From Pixabay, Content License
Saint Lucia
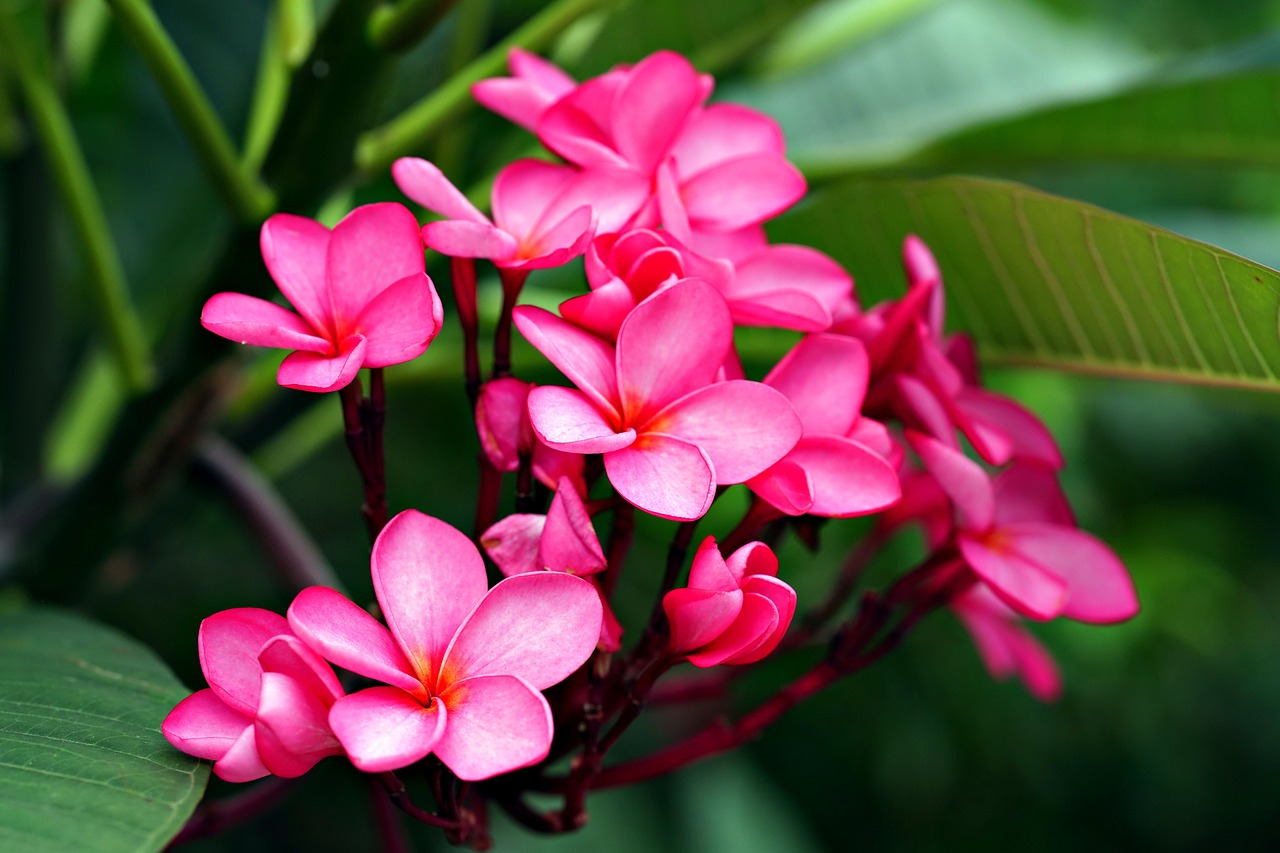
Frangipani
Plumeria

From Pixabay, Content License
General Description / Cultural Significance
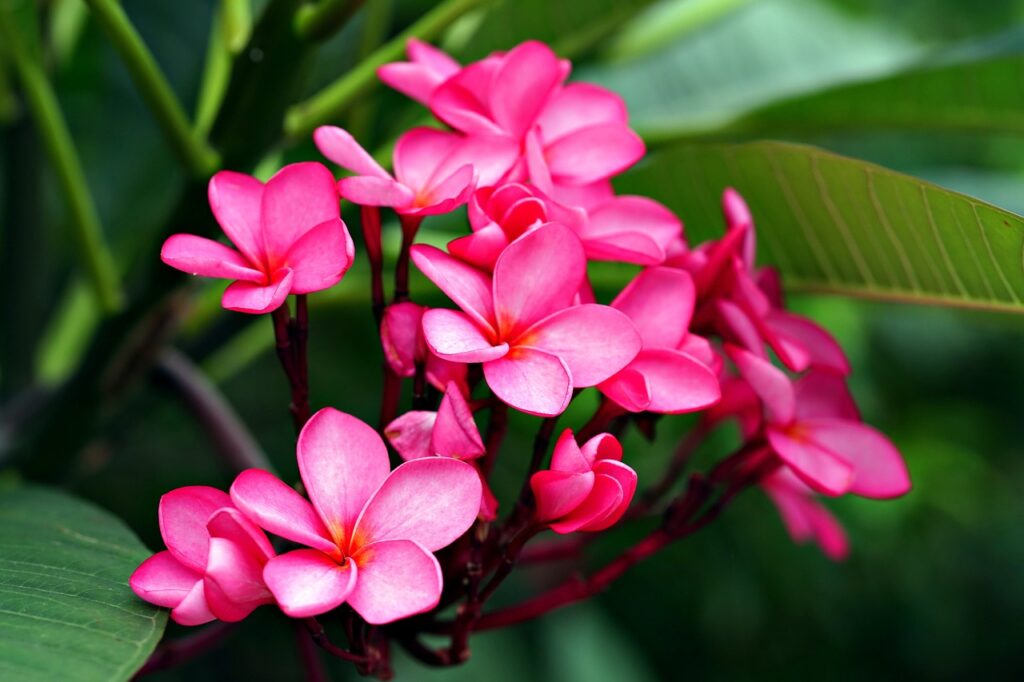
Frangipani (Plumeria) is a genus of flowering plants cherished in warm climates, especially throughout tropical regions including Saint Lucia. These captivating flowers typically bloom in vibrant shades of sunset red, bright pink, or pure white, though they can also appear in rare hues like light sky blue or violet. The blossoms exude a sweet, peachy fragrance that is most intense during the evening hours, aligning with the activity of moths, their primary pollinators. This enchanting scent that sweeps the night air, is often described as a delightful blend of sweet, floral, and fruity notes, making the frangipani a favorite in home and public gardens and in floral decor of all types.
In Saint Lucia and other Caribbean nations where Catholicism is the predominant religion, frangipani holds significant cultural value. It is believed that missionary priests, during their travels, introduced frangipanis to various parts of the world, contributing to their widespread presence on islands like Saint Lucia, St. Kitts, Thailand, and the Philippines. Beyond its intoxicating aroma, the frangipani carries deep symbolic meanings. The flower itself is seen as a representation of birth and life, while its wilting symbolizes sorrow and the inevitable transition into the winter months. Frangipani remains a key element in traditional rituals and ceremonies, such as the creation of decorative leis that serve as welcoming symbols for visitors and outsiders.
Climate Change / Conservation Status
Saint Lucia’s coastal regions, where the majority of the population resides and where tourism is heavily concentrated, are highly susceptible to the impacts of climate change, particularly sea-level rise. This vulnerability poses significant threats to the island’s ecosystem and way of life. Six species of mangrove play a crucial role in protecting the island from the effects of climate change, acting as natural barriers against erosion and saltwater infiltration.
In response to these challenges, there have been ongoing efforts to fortify the mangroves and implement additional adaptation measures to safeguard the island’s freshwater resources and coastal areas. While some projects have been initiated, more extensive and costly adaptation measures are necessary to ensure longer-term protection from the worsening effects of climate change.
Fortunately, Saint Lucia’s warm and humid climate creates an ideal environment for frangipani to flourish. The plant’s resilience and ability to thrive in this climate and handle salt spray, make it a common sight across the island, adding to the region’s natural beauty and cultural richness. However, ongoing conservation efforts are essential to preserving this and other native plant species as the island faces the increasing challenges posed by a warming world.
Alternate Names
Plumeria
Red Frangipane
Temple Tree
Sources
Descanso House Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) (Botanic Gardens Conservation
International (BGCI). “The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.” IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, IUCN, 12 June 2018, www.iucnredlist.org/species/144270910/149056540.
“Fabulous Frangipani.” Readsbyredriverbanks, WordPress, readsbyredriverbanks.wordpress.com/tag/frangipani-cultural-significance/. Accessed 9 July 2024.
“Frangipani.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, inc., 1 June 2024, www.britannica.com/plant/frangipani.
Mission of Saint Lucia to the United States. Full statement can be found on World Sensorium original website.
Zi-Ming, Sean Wang. “Plant of the Month: Frangipani – JSTOR Daily.” Plant of the Month: Frangipani, JSTOR, 16 Feb. 2023, daily.jstor.org/plant-of-the-month-frangipani/.