Cape Verde
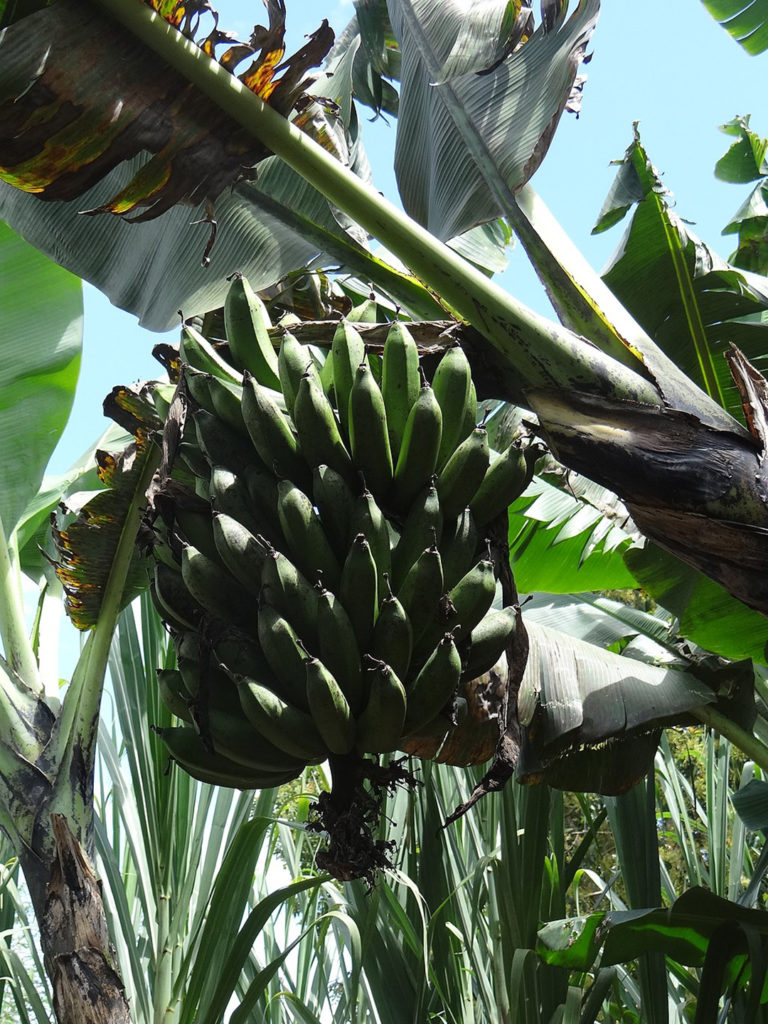
Banana
Musa Paradisiaca Sapientum

General Description / Cultural Significance
Cape Verde comprises 10 major islands off the coast of Western Africa. The geography is primarily volcanic with vegetation, including banana plants, growing mostly in fertile, moist and sunny interior valleys where they are protected from damaging winds. Banana is the most widespread of cultivated plants, and the fruit is a local staple and main export for the country.
The majority of the population lives rurally, with families cultivating the Musa Paradisiaca Sapientum primarily for their own consumption or for local trade. In addition to being a staple of subsistent farming, the M. Paradisiaca is one of the oldest cultivated plants, and all parts of the plant are used to treat medical conditions.
Climate Change/Conservation Status
The majority of Cape Verdeans live in rural areas and subsistent farm, and drought threatens their ability to even feed themselves. The extensive infrastructure protecting banana plantations from drought were destroyed in 2015 by a hurricane. However, the archipelago now faces even greater challenges due to climate change, as it is one of the nations predicted by the United Nations to disappear beneath the sea in the foreseeable future. With the tropical cyclones becoming more frequent and intense due to increasing sea surface temperatures and the sea level rise, the future of the island nation of Cape Verde is uncertain.
For now, the banana has a substantial role in everyone’s lives in Cape Verde and production is increasing as they have begun exporting bananas for the organic market. However, changing climate is predicted to change the plant’s fruit and flowering times, which may not coincide with pollinators and sea dispersals. This could change reproductive success.
Alternate Names
Sources
Embassy of the Republic of Cape Verde, Washington, D.C. This statement can be found on the World Sensorium original website.
Kumar, K. P. S., et. al., 2012. Traditional and Medicinal Uses of Banana. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, [website] 1(3), pp. 51-63. ISSN: 2278-4136
Romeiras, M. M., et al., 2010. Preservation and knowledge of medicinal plants in Cape Verde Islands: diversity and uses of exotic species since the colonization of this archipelago. Tropical Research Institute. [website]