Angola
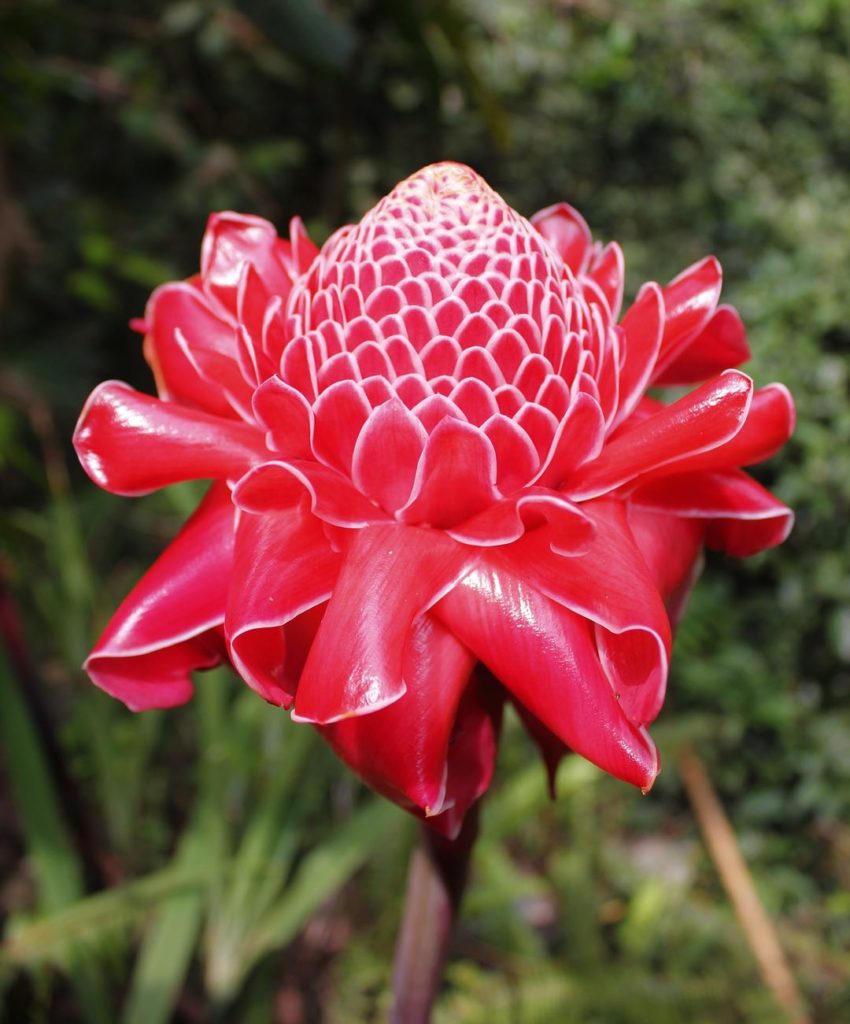
Porcelain Rose
Phaeomeria magnifica

General Description/Cultural Significance
One of the most popular flowers in Angola is the porcelain rose, Phaeomeria magnifica, which is believed to be endemic only to Angola, where it grows wild, usually close to rivers. Angola is located in southwestern Africa on the Atlantic coast. The red flower has an uncanny, artificial look and an almost unnatural ability to survive a long time after it has been cut from the plant. Angolans bring the flower into their homes as often as they can, where they enjoy its soft, ginger-like fragrance. Even though the leafy shoots of the plant are edible, it is the flower that Angolans love to gift others and to receive for its appearance and fragrance.
Climate Change/Conservation Status
Because Angola is the largest country on the African continent, its climate varies from a tropical humid to a tropical dry influenced greatly by the Atlantic Ocean on its south side. The trend has continued to be an increase in temperature and reduced precipitation, causing heat and dry stress. Climate warming is changing moisture levels and erodibility of vegetation, increasing moving sand dune fields.
The twenty-seven-year civil war that ended in 2002 devastated Angola’s agricultural region and its infrastructure, including its weather stations and the research and historical data on climate that they maintained. This loss now limits the country’s ability to understand its own historical climate vulnerability. There is no way to contextualize today’s temperatures and other climate change stressors with past patterns. But it is clear to Angolans that the ocean is warming and there are severe changes in the water cycle and weather patterns and events.
When the war ended the country’s agrarian economy, the farmers moved to cities, which not only concentrated the population on the coast lines but plunged the country into food insecurity, requiring as much as ninety-percent of its food needs to be imported. This population migration is now concentrated on the country’s coastlines, which are now plagued with rising seas, erosion and storm surges with severe infrastructure vulnerabilities. Even though there is an effort to make the agricultural sector productive, the country is in the midst of a worsening drought emergency, and there are food and drinkable water shortages.
The IUCN says that the porcelain rose has been cultivated in several protected areas in order to conserve it. Further genetic research is required in order to determine the native part of the range that exists, and to determine the size and exact status of its population.
Alternate Names
Torch Ginger
Ginger Flower
Red Ginger Lily
Torch Lily
Sources
Carvalho, S.C.P, Santos, F.D., & Pulquerio, M., 2016. Climate change scenarios for Angola: an analysis of precipitation and temperature projections using four RCMs. International Journal of Climatology, 37: pp. 3398-3412. DOI: 10.1002/joc.4925
ClimateLinks, 2018. Climate Risk Profile: Angola. US Agency of International Development. [website]
Embassy of the Republic of Angola, Washington, D.C. This statement can be found on the World Sensorium original website.
Thomas, D.S.G, Knight, M., & Wiggs, G.F.S., 2005. Remobilization of southern African desert dune systems by twenty-first century global warming. Nature 435: pp. 1212-1221. DOI: 10.1038/nature03717
United Nations Development Programme, n.d. Angola. UNDP Climate Change Adaptation. [website]