Macau
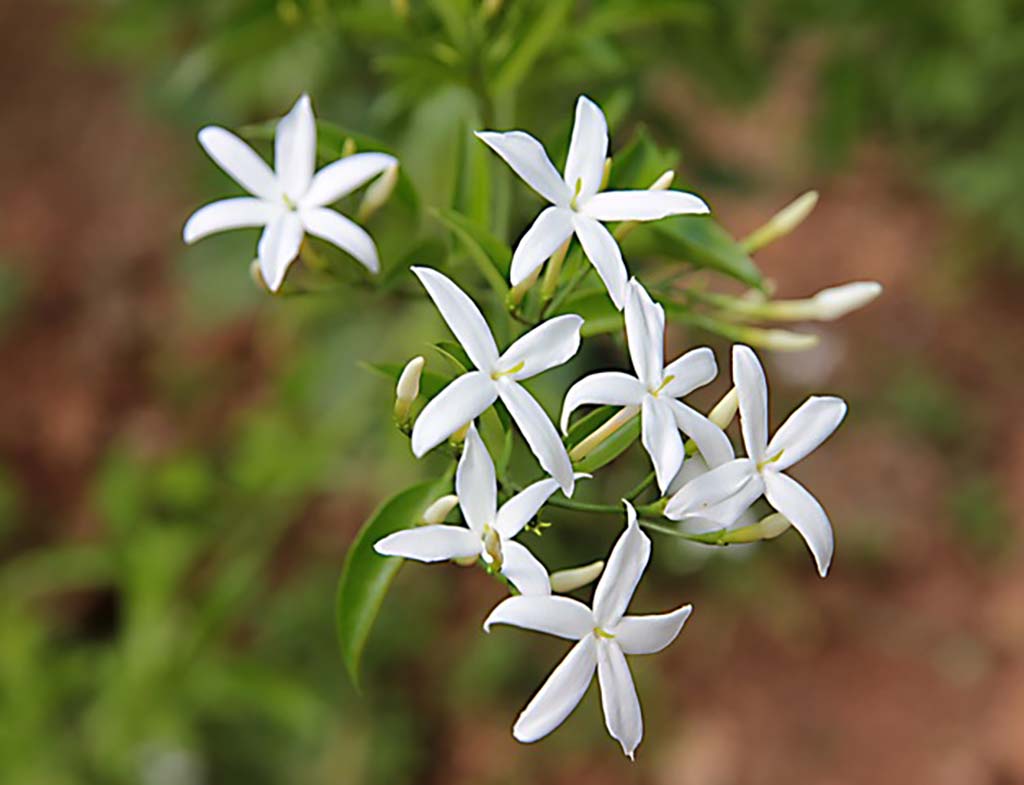
Jasmine
Jasminum

General Description / Cultural Significance
Macau, a small narrow peninsula and two islands, lies on the south coast of China, at the mouth of the Pearl River. The region consists of granite hills and small areas of flatland. These were once home to tropical evergreen forests which have since been stripped by locals who use the trees for timber and firewood. Jasmine, Jasminum, can be smelled throughout Macau: Jasmine is planted on university grounds, in public gardens and parks, and used to decorate the facades of buildings. Macau residents, just like their Hong Kongese and Chinese neighbors, have celebrated herbal tea drinking as a cultural practice for thousands of years, often enjoying the aroma, taste, and healing qualities of Jasminum as an herbal infusion. Long before modern scientists confirmed the abilities of Jasminum’s constituents, the Jasmine flower’s leaves were known throughout south China, Macau, and Taiwan as an anti-inflammatory and an antibacterial while the flower was known as an antifungal agent. For the mostly Buddhist population of Macau, Jasmine has a spiritual significance as a plant described by Buddha as “the fragrance of virtue.” Jasmine incense is lit before Buddhist shrines with special meaning during prayer and reflection.
Climate Change / Conservation Status
Macau is highly exposed to climate change as it resides barely above sea level and is subject to tidal inundation and massive flooding during extreme weather events. The country is also one of the most densely populated regions in the world, raising the stakes as the threat of extreme weather events intensifies. Typhoon Hato hit Macau in 2017 and devastated the city’s infrastructure and tourism industry. Macau’s sea level is now rising at an accelerated rate, exacerbated by the country’s very low elevation, high coastal development, and dense population. City developers are working to utilize land effectively and sustainably as the people of Macau attempt to reconcile a growing tourism industry with the consequences of climate change and an ecosystem in dire need for conservation. Macau’s remaining Jasmine is grown in gardens such as The Ecological Trail Garden of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants and South China Medicinal Plants Garden. All flora is vulnerable to the increased flooding and impacts of climate change.
Alternate Names
Summer Jasmine
Poet’s Jasmine
Sources
China Culture Tour, 2019. Herbal tea in Hong Kong and Macau. China Culture Tour. [website]
Conneller, P., 2019. Macau and its casinos face uncertain future due to climate change. Casino.org. [website]
Dhammika, B.S., Incense. Guide To Buddhism A To Z. [website]
Dspa.gov.mo, 2022. Report on the State of the Environment of Macao. [website]
IAM.gov, 2020. Ecological trail garden of medicinal and aromatic plants and South China medicinal plants garden. Government Office in the Municipality of Macau, Macao. [website]
Jaya Prakkash, M.A., Ragunathan, R. & Jesteena, J., 2019. Evaluation of bioactive compounds from Jasminum polyanthum and its medicinal properties. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 9(2): 303–310.
Leafy Place, 2021. Types of jasmine flowers: Amazing varieties of Jasmine Plants. Leafy Place. [website]
Liang, Z., 2020. Analysis of Plant Landscape Planning in Macau Universities—Taking Macau University of Science and Technology as an Example. Landscape and Urban Horticulture , 2: 12–24.
Mulhern, O., 2020. Sea level rise projection map – Zhuhai & Macau. Earth.Org. [website]
Shane, W., Spratt, D., 2016. How climate change will sink China’s manufacturing heartland. Climate Code Red. [website]