Wikimedia, Androstachys, CC BY-SA 3.0
Sint Maarten
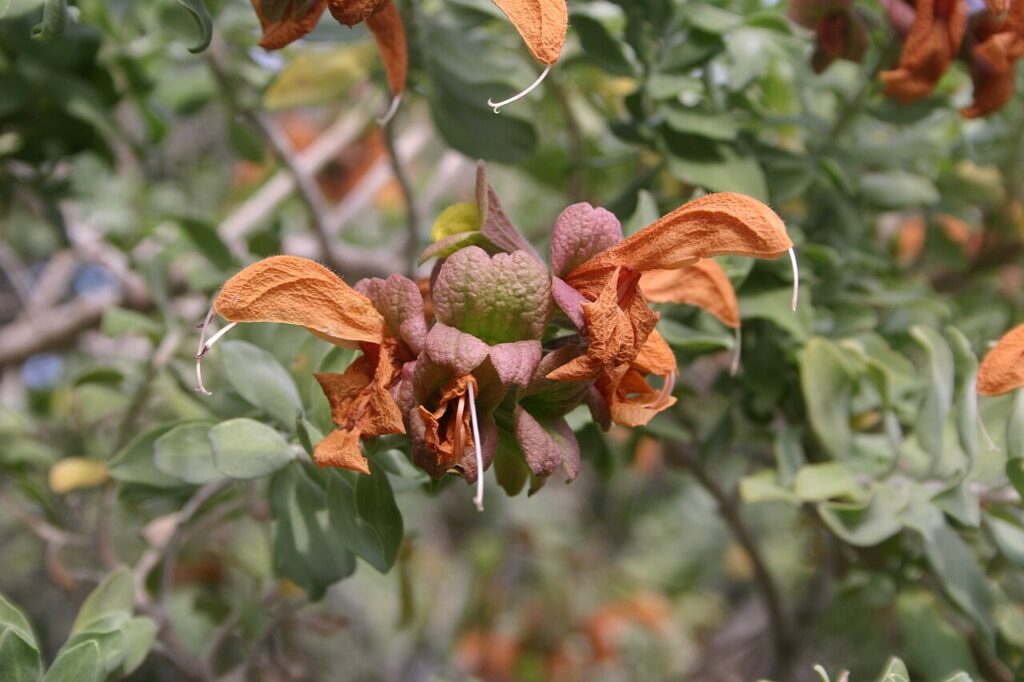
Orange-Yellow Sage
Salvia aurea

Wikimedia, Androstachys, CC BY-SA 3.0
General Description / Cultural Significance
Orange-Yellow Sage (Salvia aurea), also known as Beach Sage or Golden Sage, is a resilient and aromatic shrub originally native to southern Africa. Over time, it has been introduced to various regions, including the Caribbean, where it has naturalized in coastal environments like those of Sint Maarten. Adapted to sandy, well-draining soils and capable of withstanding high salinity, this hardy species is a common sight along the island’s shorelines.
Characterized by its silvery-green foliage and striking golden-yellow flowers, Salvia aurea enhances the natural beauty of Sint Maarten’s landscapes while supporting biodiversity. The plant is particularly attractive to pollinators, including bees and butterflies, which play a crucial role in maintaining the island’s delicate ecosystems. Its ability to thrive in nutrient-poor soils and withstand drought conditions makes it a favored choice for xeriscaping and sustainable landscaping efforts.
In Sint Maarten, Orange-Yellow Sage is valued not only for its ornamental appeal but also as a symbol of resilience and adaptability—qualities that resonate with the island’s natural and cultural heritage. While it does not hold deep-rooted medicinal traditions on the island, as some other sage species do, its aromatic properties are appreciated in local gardens and green spaces. The plant’s presence in both wild and cultivated settings represents a harmonious balance between introduced species and the island’s endemic flora, reflecting the broader ecological and cultural diversity of Sint Maarten.
Climate Change / Conservation Status
Although Salvia aurea is not native to Sint Maarten, it has successfully adapted to the island’s coastal and arid environments. However, like many plant species in the Caribbean, it faces indirect threats due to climate change. Rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and an increase in extreme weather events—such as hurricanes—pose challenges to its long-term stability. Coastal erosion, exacerbated by stronger storm surges and shifting tides, can impact the sandy habitats where this species thrives. Additionally, a decline in pollinator populations due to habitat disruption could affect its reproductive success.
Despite these challenges, Salvia aurea remains a resilient species, and its ability to endure harsh conditions makes it an important component of coastal vegetation in Sint Maarten. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting coastal ecosystems, mitigating soil erosion, and supporting pollinator populations will contribute to the continued presence of this adaptable plant on the island.
Alternate Names
Beach Sage
Golden Sage
Sources
“Salvia Koyame.” Salvia Koyamae – Plant Finder, Missouri Botanical Garden, 2023, www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=292463#:~:text=Noteworthy%20Characteristics,excellent%20foliage%20and%20yellow%20flowers.
Yokoyama, Mark. “Three Flowers.” Association Les Fruits de Mer, Les Fruits de Mer, 27 Feb. 2020, www.lesfruitsdemer.com/three-flowers/.