Tree Planting Guide
Store your tree
It is important to temporarily keep your seedling or sapling in a cool, dry place, and keep the roots moist until planting day. Make sure it gets sunlight during this time. Your tree has the best chance for survival if it is planted soon after adoption. Spring and early summer are the best periods to plant trees.
Where to plant your tree
First, plant a tree native that is suited to the area where it will live. The four tree species offered by WS/C are all native to the northeast. One good place to plant your tree is in your own yard, or on other private property with permission of its owner, which could be a relative or close friend. With permission from the right agency, your native tree might be able to be planted on public land managed by a city, state or federal government.
Prepare the soil
Once you’ve picked your site based on the tree’s needs and growth projection, you should prepare the soil. If your earth is naturally heavily compacted, you may want to add some local, organic matter such as manure or compost to the native soil planting area. Don’t use fertilizer, potting soil, or chemicals as these will kill your young tree.
Create the hole
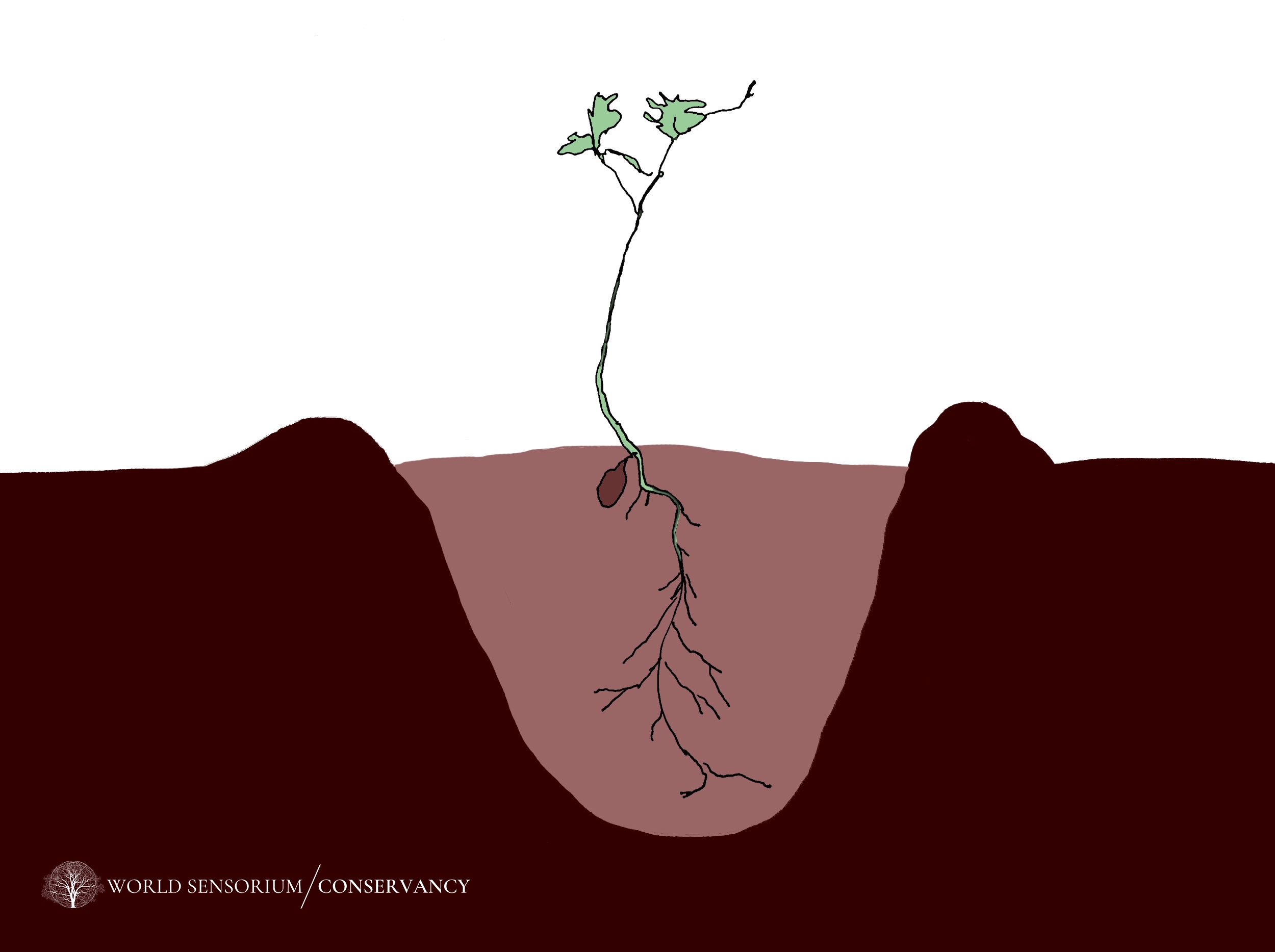
Dig a round hole that is at least one foot in diameter or, if it is a container tree, 3-4 times the width of the container soil. If your tree is in a root ball, the hole depth should be equal to the height of the root ball. Loosen soil around the edges of the hole to make it easier for the tree’s roots to spread. The hole should have sloping sides leading to the bottom.
Look at your tree and assess where the root flare is located (the point on the plant where roots start branching out). This root flare will need to be level with the surrounding ground soil by the time you have filled your hole and finished planting your tree. To ensure the root hole ends up at the proper depth in the soil–not too deep below the ground or too exposed above the soil level–create a mound of loose soil of the approximate proper height, at the bottom of your hole.
Plant your tree
Carefully remove the tree from its container or burlap wrapping, paying special attention not to damage the roots.
Set your tree in the center of the hole. If the tree has bare roots, gently spread them out over the small mound of soil, covering the roots completely. If the roots of the tree are surrounded by container soil, simply set the plant on top of the soil mound.
Seedling or
Sapling
times wider than the
container or soil ball.
Use native soil to fill in the hole.
Fill the hole halfway with soil and tamp down. Next, fill the hole halfway with water.
After the water has soaked in, fill the hole the rest of the way with soil, ensuring that the root flare of the tree begins just above the surrounding soil level or ground. Avoid planting saplings too shallow or too deep. Sometimes this means holding up the tree and adding some loose soil, or backfilling, until your tree is at the right depth. When you are done, make sure the filled soil around the tree is level with the surrounding ground.
As you complete this last step, avoid tamping down the wet soil as this removes oxygen that the tree’s roots need.
Add water and mulch
Create a slightly elevated soil rim around the perimeter of the hole to form a basin for your tree’s water. Generously water the new tree with a bucket hose or sprinkler. This should settle the top layer of soil.
Lastly, apply mulch 1-3 inches deep around the tree, but not up against the trunk.
Add protection
It is best to install a tree guard or fence around the perimeter of the tree. These can be purchased online and at gardening stores, or can be handmade. While the tree is small, the first protector can be made out of recycled plastic bottles by cutting off the tops and bottoms. This will protect the tree from being inadvertently damaged by landscaping equipment or eaten by wildlife.
Maintain your tree
Water your tree daily for the first 2 months, and weekly for the next 6 months. Keep a tree guard around the tree for the next 2 years. Keep mulch around the tree to help the tree retain moisture, but do not mound the mulch. Weed and remove grass around the tree regularly.
Growing your Tree in a Container
If you can’t find a place to grow your tree in the ground right now, planting it in a container is popular way to grow your tree in the city. Container-grown trees can be placed on rooftops, balconies, patios, porches and sometimes on street level outside entry to your building.
Always make sure the bottom of the tree’s container has good water drainage holes before you start planting and that the container is deep enough to accommodate the tree’s growing roots and wide enough to provide good soil insulation. The weight of the container with soil and watering must be taken into account when locating your tree. Use large heavy containers for places where the tree can remain outdoors throughout the year. When planting the tree, use compost enriched soil purchased from a nursery or garden center to fill the container. Water and fertilize regularly and add some new enriched soil yearly.