From https://pixabay.com
São Tomé and Príncipe
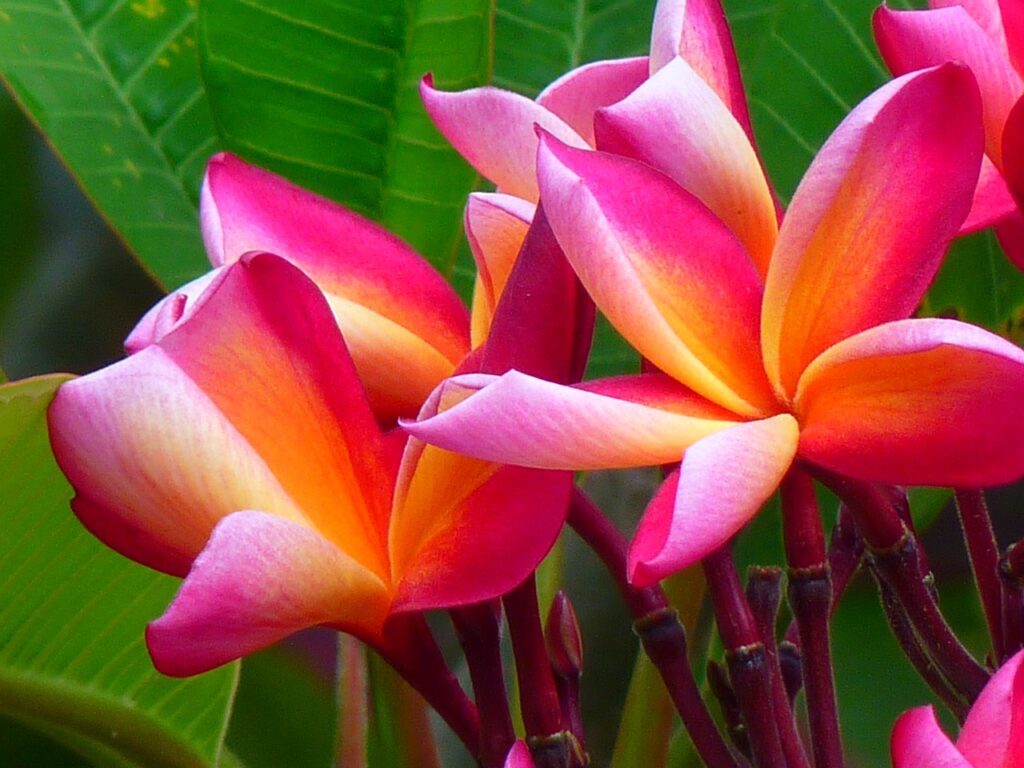
Frangipani
Plumeria

From https://pixabay.com
General Description / Cultural Significance
The Frangipani (Plumeria) is a genus of flowering trees widely recognized for its vibrant, tropical appearance and captivating, honey-like fragrance, which intensifies in the evening. The leaves are large, glossy, and typically range from 12 to 18 inches in length, creating a lush backdrop for the flowers. Frangipani blooms are the tree’s most distinguishing feature, presenting an array of colors from white and pink ombre to vivid shades of red and yellow. The flowers’ distinctive shape, combined with their delicate fragrance, makes them particularly beloved across the tropics. The tree itself can vary in height from 6 to 33 feet, depending on the environment and care it receives.
Frangipani is native to tropical and subtropical regions, thriving in warm, sunny climates with well-drained, slightly acidic soils. In São Tomé and Príncipe, the climate is ideal for these trees, which flourish under consistent heat and sunlight. Unlike many flowering trees, mature frangipanis are resilient, with a notable drought tolerance that allows them to endure dry spells once established.
The volcanic islands of São Tomé and Príncipe, a former Portuguese colony, have been referred to by naturalists as “Africa’s Galapagos”. In 2012 UNESCO designated much of the small island nation as a UNESCO biosphere reserve protecting its sixteen species of endemic birds, sea turtles, tropical forest, and rare flora. There, frangipani has deep cultural and symbolic value and most religious and social events include frangipani The flower represents beauty, renewal, and the hope for prosperity—a meaning it shares across many tropical cultures. Frangipani flowers are often woven into local customs, including adornments for celebrations, ceremonial offerings, and even daily wear, as they are frequently worn in the hair or used in leis. The tree’s longevity and year-round blooming also make it an emblem of resilience and natural beauty on the islands, enhancing gardens, public spaces, and cultural gatherings.
Frangipani’s fragrance is complex, evoking a blend of floral and fruity notes with undertones of jasmine and citrus, which gives it a distinctive and alluring scent profile. The essential oils derived from frangipani flowers are highly sought after in the perfume and aromatherapy industries for their relaxing and mood-enhancing properties. Chemical analysis of frangipani essential oil reveals a combination of terpenoids, including linalool, geraniol, and citronellol, which contribute to its sweet and calming scent. These compounds have shown antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and even mild sedative effects, making frangipani valuable for use in holistic therapies and wellness practices.
Beyond its ornamental appeal, frangipani has practical applications in São Tomé and Príncipe’s traditional medicine. In folk remedies, the bark and leaves have been used to treat ailments such as fevers, headaches, and digestive issues, although proper preparation is essential as some parts of the plant can be mildly toxic. In low doses and with careful preparation, extracts of frangipani are utilized to soothe skin irritations and reduce inflammation, demonstrating its multifaceted role in local healing practices. However, caution is advised, as ingestion of raw plant parts can cause nausea or other symptoms, underscoring the importance of knowledge in its medicinal application.
Climate Change / Conservation Status
Due to São Tomé and Príncipe’s stable tropical climate, frangipani faces minimal immediate risk within the country. The natural conditions on the islands support its growth year-round, and frangipani continues to thrive without significant threat. However, ongoing climate changes, particularly shifts in rainfall patterns or extreme weather events, and coastal erosion could potentially impact the tree’s health in the future. Conservation efforts may not be urgent at present but ensuring the protection of local biodiversity and the ecosystems supporting plants like frangipani is essential to maintaining the ecological balance of São Tomé and Príncipe in the face of climate change.
Alternate Names
Plumeria
Plumeria rubra
Nosegay
Sources
Mahr, Susan. “Plumeria.” Wisconsin Horticulture, University of Madison Wisconsin, 2024, hort.extension.wisc.edu/articles/plumeria/.
Petruzzello, Melissa. “Frangipani.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, inc., 20 Sept. 2024, www.britannica.com/plant/scabious.
Zi-Ming, Sean Wang. “Plant of the Month: Frangipani – JSTOR Daily.” Plant of the Month: Frangipani, JSTOR, 16 Feb. 2023, daily.jstor.org/plant-of-the-month-frangipani/.
Permanent Mission São Tomé and Príncipe to the United Nations.
“Reducing Vulnerability in São Tomé and Príncipe”.