Guatemala
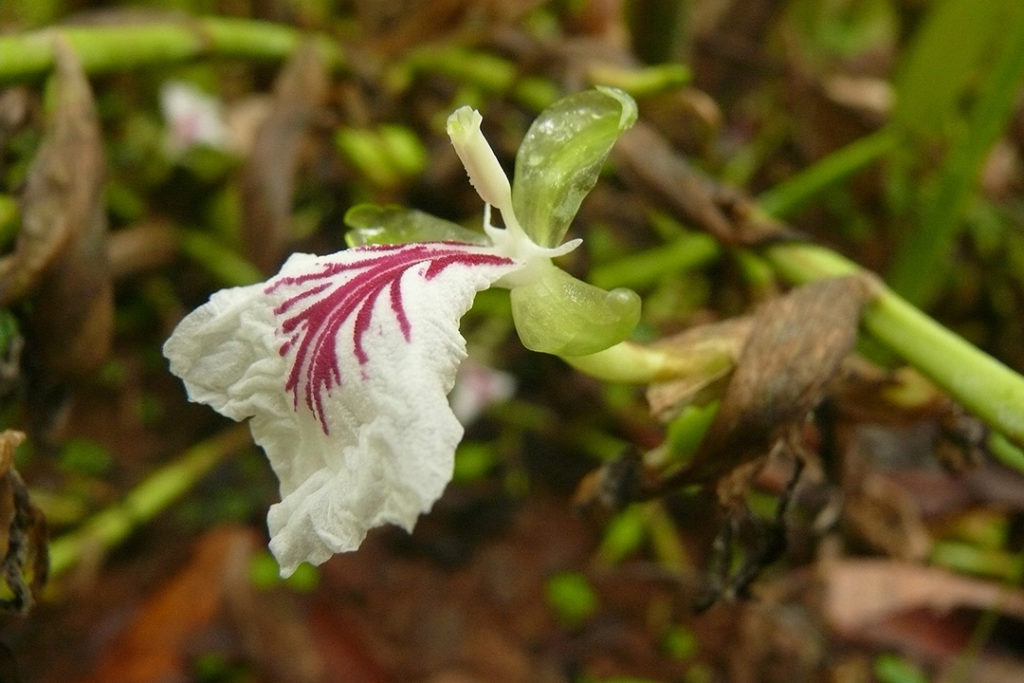
Cardamom
Elettaria cardamomum and Amomum

General Description / Cultural Significance
Guatemala is one of the biggest producers of cardamom in the world, second to India. The seeds of cardamom, Elettaria cardamomum and Amomum is a pungent herbaceous plant from the ginger family, with white or pale purple flowers and long pointed leaves. The plant is ground and used both as a condiment and as a therapeutic medicine. It flavors coffee and baked goods, freshens breath, and is found in chewing gum specifically in Guatemala. It also treats stomach problems, sore throat, indigestion, and nausea. It is known to be one of the most valued spices in the world, with aromatic foliage that produces a soothing smell and taste, earning its name as “Queen of Spices.”
Climate Change/Conservation Status
Research on sustainable cultivation of cardamom published in 2006 found that although cardamom cultivation is proven to be an excellent resource for countries such as Guatemala, all countries growing the plant have shown that deterioration of their primary forest is common. Guatemala is a biodiversity-rich country that has harmed their endemic species within the forest from cardamom growing practices. It is suggested that more sustainable cultivation methods be used to reduce the harmful impact to biodiversity.
From 1996 to 2015 Guatemala was reported to be one of the top ten countries most affected by climate change, and this continues. The natural disasters that climate change brings about are impactful on Guatemala because of its geographical location, which is within an earthquake and hurricane zone, and the country’s inhabitants, who are subject to periods of malnutrition and tend to have inadequate housing. Deforestation continues to be one of Guatemala’s main environmental problems affecting not only its coffee production, but its cardamom production as well. Coffee rust disease is affecting both plants due to the fact that too many trees have been cut down within the forest. The country is currently trying to pass stronger legislation to help the environment and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change within the country.
Although Elettaria cardamomum is not reported as endangered at this time, Guatemala has had very poor crop yields due to climate change. Ongoing drought and increasing famine are primary factors for migration to the United States.
Alternate Names
Green cardamom
True cardamom
Sources
Ambassador’s Office, Permanent Mission of Guatemala to the United Nations. This statement can be found on the World Sensorium original website.
CCAFS, n.d. Latin America. Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security. [website]
Missouri Botanical Garden, n.d. Elettaria cardamomum. Missouri Botanical Garden. [website]
Reyes, T., Luukkanen, O., & Quiroz, R., 2006. Small cardamom—precious for people, harmful for mountain forests: possibilities for sustainable cultivation in the east Usambaras, Tanzania. Mountain research and development, [website] 26(2), pp. 131-137.
Sow Exotic, n.d. Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum). Sow Exotic. [website]
The Tico Times., 2013. Guatemala: Adapting to climate change. The Tico Times. [website]
Tran, M., 2013. Trouble brewing in Guatemala’s coffee and cardamom fields. The Guardian. [website]
Waddick, K., 2017. Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture in Guatemala and Honduras. Global Majority E-Journal, [website] 8(2), pp. 109-120.