Forest & Kim Starr, CC BY 3.0
Rwanda
Coffee
Coffea

Forest & Kim Starr, CC BY 3.0
General Description / Cultural Significance
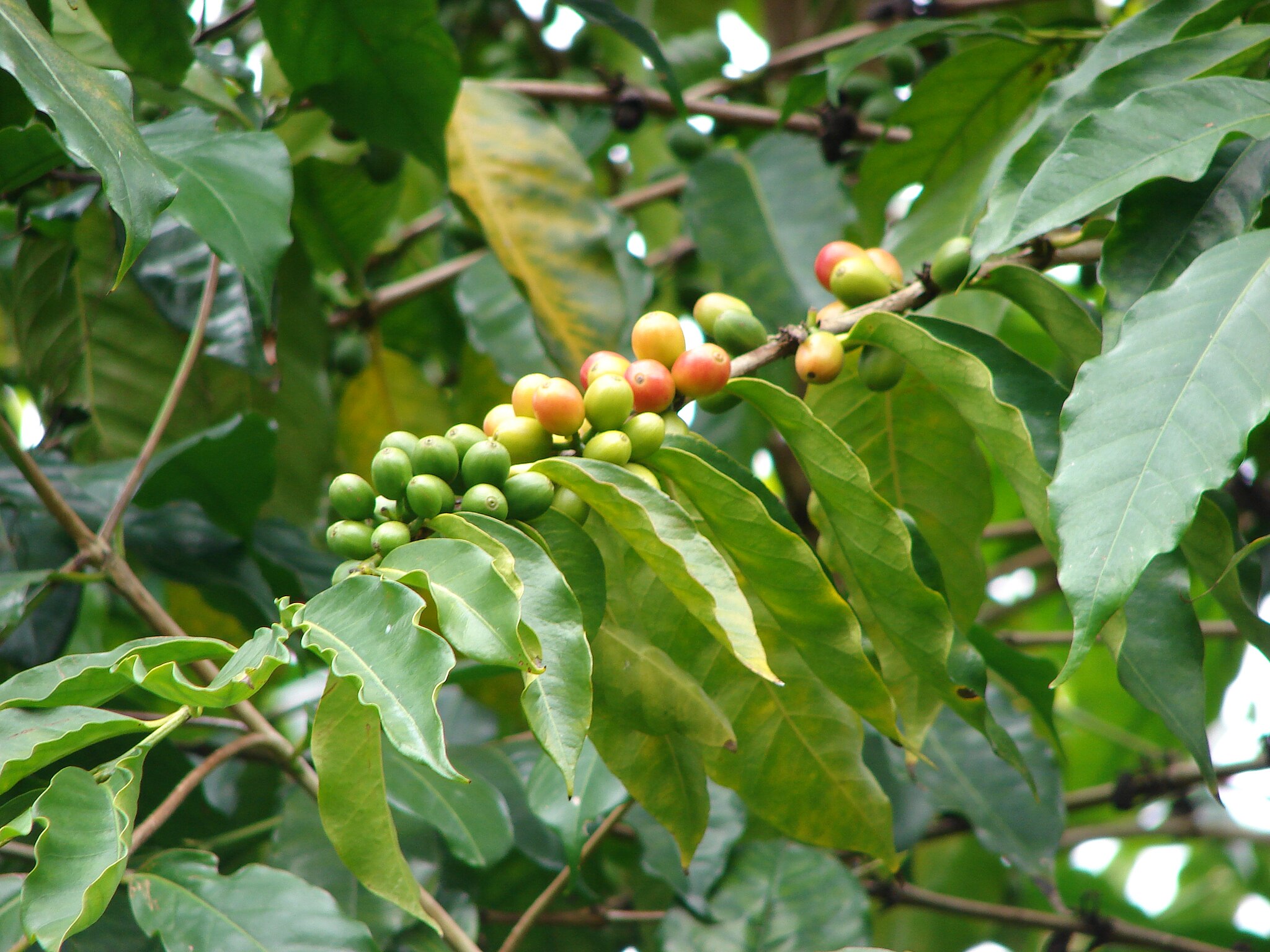
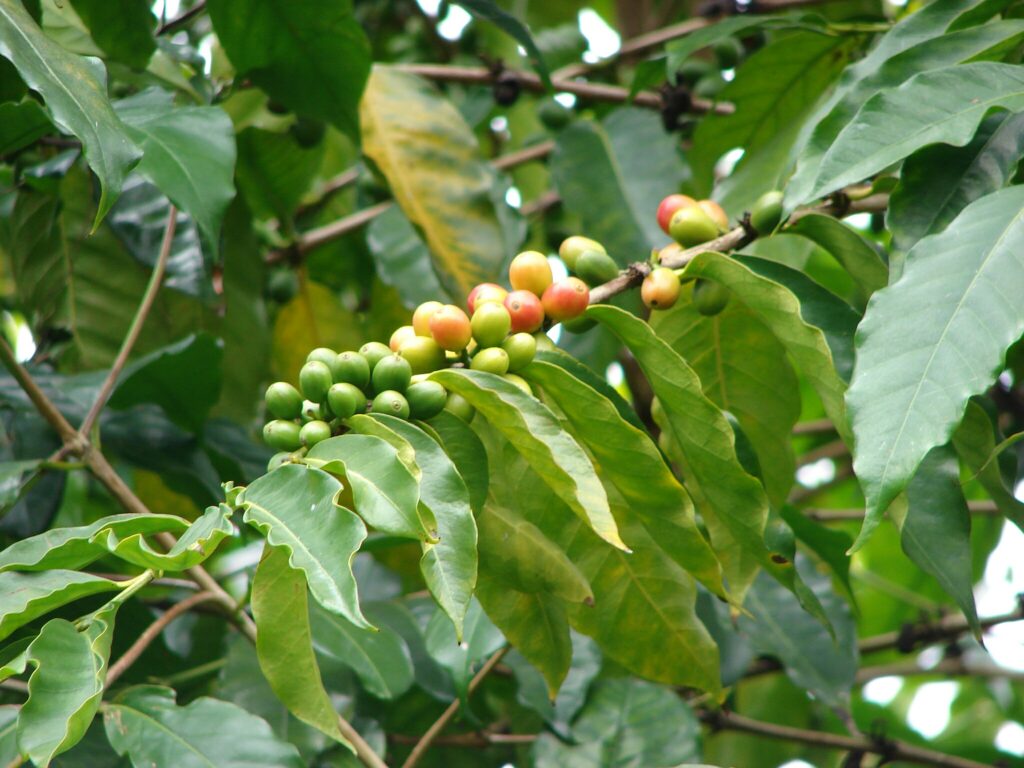
Rwanda’s rolling high-altitude hillsides offer great conditions for growing Coffee plants. Since the early 20th century, Coffee exportation has been integral to Rwandan culture and socioeconomic progress. Following the devastation and economic hardship caused by the 1994 Rwandan genocide, Coffee became a key tool in rebuilding the Rwandan economy. The government ensured and secured efforts to grow the Coffee industry across the nation. Today, Rwandan coffee, especially Bourbon varieties, are the nation’s chief crop, providing income for thousands of small farmers, and accounting for half of the country’s exports.
Known for its high quality, fruity taste, and medium to full-bodied roast, Rwandan Coffee is cultivated and distributed across the nation. There are many different types of Coffee produced in Rwanda, such as Bourbon, Typica, Red Catuai, Blue Mountain, and Yellow Catuai. Rwandan Coffee is notorious for its scent bright in citrus fruits including orange blossom and lemon. Many locals now prepare, and drink coffee, and coffee culture and cafes are rapidly growing. The appreciation of coffee has moved from the beautiful scent of the coffee flower and the processing of the bean, to the love of the aroma of freshly brewed premium local coffee, the nation’s most significant scent.
Climate Change / Conservation Status
Rwandan agriculture has experienced increased rainfall, flooding, net-area loss, and disease due to recent changes in climate. Coffee production has been heavily impacted by such changes, for example, cherry development and flowering are negatively affected by the poor environments. In 2022, there was a 5% decrease in Coffee production across the nation due to climate change.
Looking ahead, Coffee production in the Eastern Province of Rwanda is likely to be the most impacted by changes in climate since droughts are more likely to occur in this area of the nation. Regenerative agriculture is necessary for the country to improve yields and replenish soil. The introduction of shade trees to Coffee plots could help Rwandan land to adapt to changes in climate and reduce damage caused by floods and heavy rainfall.
Alternate Names
Coffea
Sources
Office of the Ambassador, Mission of the Rwandese Republic to the United Nations. This statement can be found on the World Sensorium original website.
2023. Rwandan Coffee: A Comprehensive Guide. Advise Coffee. Available from https://advise.coffee/rwandan-coffee/#:~:text=For%20example%2C%20coffee%20in%20Rwanda,the%20country’s%20largest%20cash%20product
2022. What Can You Pair With the Rwanda Coffee Flavor Profile? Coffee Blenders. Available from https://www.coffeeblenders.com/blogs/news/what-can-you-pair-with-the-rwanda-coffee-flavor-profile#:~:text=The%20Rwanda%20coffee%20flavor%20profile%20is%20described%20as%20a%20full,lemon%2C%20and%20other%20citrus%20fruits
Coffee Production in The Face of Climate Change: Rwanda. Sustain Coffee. Available from https://www.sustaincoffee.org/assets/resources/Rwanda_CountryProfile_Climate_Coffee_6-7.pdf
Iliza, A. 2022. Changing weather patterns take toll on coffee production. Rwanda Today. Available from https://rwandatoday.africa/rwanda/news/changing-weather-patterns-take-toll-on-coffee-production-3722448
Hefferon, R. 2021. Regenerative Agriculture Is Helping This Coffee Co-op Fight Climate Change. Root Capital. Available from https://rootcapital.org/regenerative-agriculture-is-helping-this-coffee-co-op-fight-climate-change/