From Pixabay, photo by Peggy_Marco, Content License
Saint Barthélemy
Frangipani
Plumeria

From Pixabay, photo by Peggy_Marco, Content License
General Description / Cultural Significance
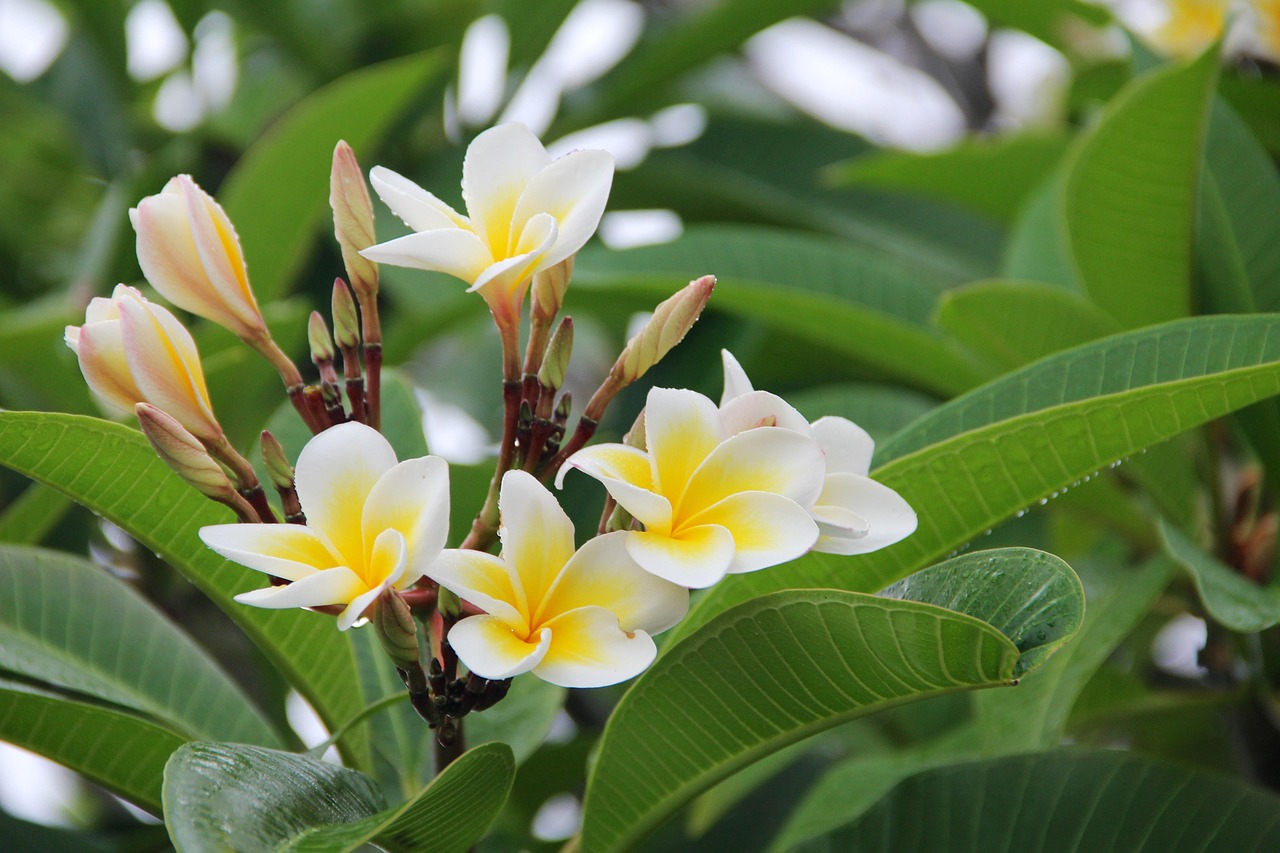
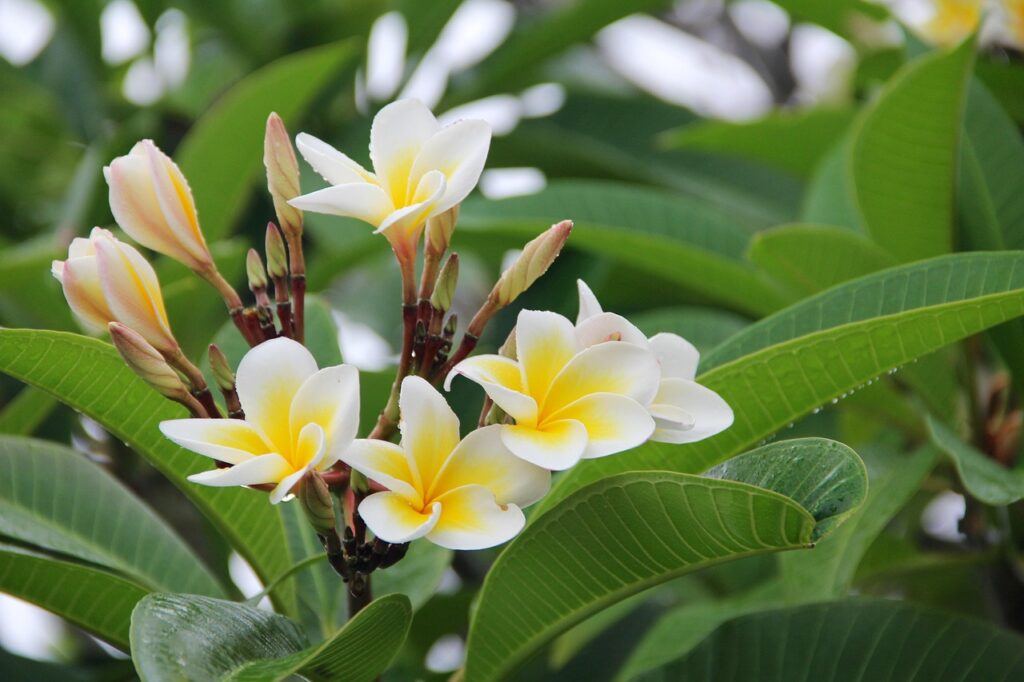
Frangipani (Plumeria) is a tropical flowering plant renowned for its sweet, intoxicating fragrance and vibrant blossoms, which range in hues from pink, red, and yellow to pure white or cream. The flowers, with their smooth, waxy texture, help the plant retain moisture in the hot, at times arid, tropical climate. Their scent, a rich blend of peachy and floral notes, becomes most pronounced in the evening, coinciding with the emergence of nocturnal pollinators such as moths.
In Saint Barthélemy, frangipani is a beloved aromatic plant, frequently used in leis to welcome visitors and incorporated into decorations for social and religious gatherings. It holds deep cultural significance across the Caribbean, symbolizing love, beauty, and new beginnings. This symbolism makes frangipani a favored choice for weddings, where it is believed to bring good fortune and prosperity to newlyweds.
Beyond its decorative and symbolic roles, frangipani is also highly valued for its aromatic properties. Its richly scented blossoms release a sweet, heady fragrance that lingers in the air, creating an ongoing immersive experience. This distinctive scent not only enhances the natural beauty of the island but also contributes to its unique olfactory identity, evoking memories and emotions tied to the landscape. Whether carried by the ocean breeze or concentrated in gardens and village pathways, the fragrance of frangipani plays an essential role in defining the island’s sense of place.
Frangipani has been used in traditional medicine across various cultures, including in the Caribbean, for its purported therapeutic benefits. The plant contains bioactive compounds such as alkaloids, flavonoids, and iridoids, which have been studied for their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial properties. In folk medicine, extracts from frangipani bark, leaves, and flowers have been used to treat conditions such as skin ailments (wounds, ulcers, and insect bites, fever and respiratory infections, pain relief, and digestive health.
In modern wellness practices, frangipani essential oil is widely used in aromatherapy, where its calming scent is believed to reduce stress, improve mood, and promote relaxation. Its hydrating and soothing effects also make it a key ingredient in luxury skincare products and perfumes.
Climate Change / Conservation Status
Although frangipani is not currently classified as endangered or threatened in Saint Barthélemy, it faces ecological pressures. Besides climate change, one of the primary threats is the Plumeria mealybug (Maconellicoccus hirsutus), an invasive pest that feeds on frangipani trees, leading to defoliation, weakened growth, and reduced flowering.
Additionally, the increasing footprint of tourism and urban development poses a long-term risk to the island’s native and ornamental flora. While frangipani is resilient, ongoing conservation efforts—including pest management strategies and sustainable landscaping practices—are essential to maintaining its presence in Saint Barthélemy’s natural and cultural landscape.
Alternate Names
Plumeria
Dok Champa
Red Frangipane
Temple Tree
Sources
Norwood, FA. “The Ultimate Plumeria Care Guide.” The Ultimate Plumeria Care Guide, 19 Aug. 2023, plumeriacareguide.com/about-the-plumeria/origin-and-native-regions-where-plumeria-are-found/plumeria-in-the-caribbean/.
Tiernan, Nicole, et al. “Phylogenetic Relationships of Cuban and Caribbean Plumeria …” Phylogenetic Relationships of Cuban and Caribbean Plumeria (Apocynaceae) Based on the Plastid Genome, 19 Aug. 2023, academic.oup.com/biolinnean/article/140/3/397/7246402.